The Laboratory
facilities

IoT Testing Laboratory

Pilot area

Virtual Reality Laboratory
Areas
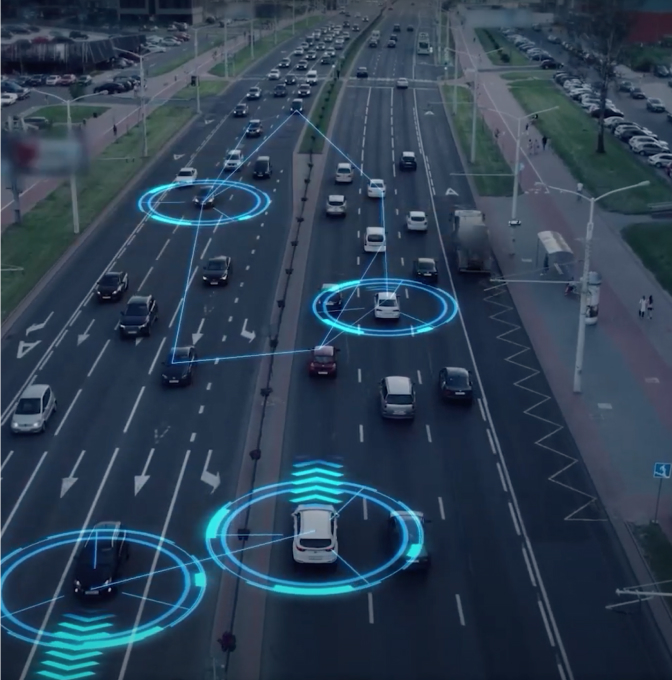
IoT technology can be used in a wide variety of smart services in a city to improve the efficiency and effectiveness of municipal public services.
Our activity
The researchers participating in the IoTMADLab form a multidisciplinary team that represents the union of two of the main research lines of CEDINT-UPM: Internet of Things and Energy Efficiency (IoT-EE) and Virtual Reality and Data Visualization (VR).
The Laboratory and its network
The way technology is applied to city services and the very governance of ICT are in a process of transformation in which people are at the center of the digitization processes.
In this regard, Madrid has signed the Living-in.eu initiative declaration for a sustainable digital transformation of European cities and communities. In this framework, the Digital Office of the City Council actively participates in working groups such as the one related to UserCentriCities in which people are an integral part of the co-design of digital services.
On the other hand, CEDINT-UPM and the Universidad Politécnica de Madrid collaborate with various laboratories and international research centers to deploy in real scenarios the latest technological advances for the benefit of citizens.
Documents

Categories
Media coverage
The advances of our laboratory have aroused the interest of many media outlets, both general and specialized::
Funding
Every year, the technical secretariat of the Madrid Business FORUM asks the municipal areas for public-private cooperation projects interesting for the city, the economy and companies.
After studying, a first selection is made. The chosen projects are presented to the representatives of the forum companies by the municipal officials. Finally, companies vote and choose the projects to be carried out each year.
In 2021, the Digital Office presented a project that was selected by the FORUM as one of the most appreciated funded projects by company representatives. The Internet of Things Laboratory of the city of Madrid, IoTMADLab, concretizes this initiative, and the first results are presented on 22 November
With its funding, the Madrid City Council has signed a collaboration agreement with the Center for Integral Home Automation (CEDINT) of the Polytechnic University of Madrid to support the Laboratory.
At the end of 2022, another project was proposed, which extended the scope of the previous one, allowing additional financing, through an addendum to the agreement, to incorporate 5G technology and enhance the specific cybersecurity aspects of these specialties.